Home / Segmental Osteotomies
Drop Your Number here
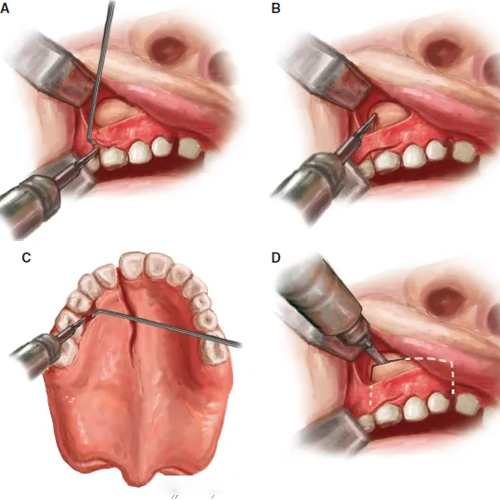
Segmental Osteotomy is a specialized jaw surgery technique where the jawbone (maxilla or mandible) is divided into smaller segments and repositioned to correct localized dental or skeletal deformities. Unlike full jaw movement, this approach allows for more precise corrections of smaller sections of the jaw — especially useful in complex orthodontic cases or when traditional braces alone are insufficient.
It is commonly used to treat issues like spacing, open bite, asymmetry, or excessive jaw length in a very focused and controlled manner.
What We Do
Our surgical team performs both Maxillary Segmental Osteotomies and Mandibular Segmental Osteotomies, depending on the location and nature of the deformity. Each procedure is custom-planned using CBCT scans and cephalometric analysis to achieve ideal occlusion, alignment, and aesthetics.
Commonly performed segmental procedures include:
Anterior Segmental Osteotomy – To reduce excessive protrusion or spacing
Posterior Segmental Osteotomy – For molar correction or posterior open bite
Vertical Segmental Osteotomy – To correct excessive vertical dimension
Segmental Maxillary Impaction – For long face syndrome and gummy smiles
Who Needs Segmental Osteotomy?
Patients with localized dental misalignment
Individuals with open bite or deep bite not treatable with braces alone
Adults with skeletal discrepancies in limited jaw regions
Those with excessive dental show or protrusion in anterior teeth
Complex orthodontic cases requiring surgical assistance
Benefits of Segmental Osteotomies
Highly targeted correction without moving the entire jaw
Reduces need for extensive bone movement
Enhances dental alignment and bite correction
Minimizes relapse risk when combined with orthodontics
Can address aesthetic concerns like protruding teeth or gummy smile
Useful in relapse correction after failed orthodontic or jaw surgeries
Surgical Process
Preoperative orthodontics (if needed)
Digital planning with 3D imaging and dental models
Surgery under general anesthesia
Precise bone segment cutting, repositioning, and fixation
Stabilization with titanium mini plates and screws
Post-op healing and continued orthodontic alignment
Recovery & Aftercare
Mild swelling, discomfort, and numbness for 7–10 days
Soft diet and oral hygiene maintenance for 2–4 weeks
Full healing in 6–8 weeks
Post-operative orthodontic fine-tuning (if applicable)
Risks & Considerations
Risk of root damage if not planned carefully
Temporary numbness or swelling
Possibility of minor asymmetry or need for secondary adjustments
Surgical precision and experience are crucial for long-term stability