Home / Hemifacial Microsomia
Drop Your Number here
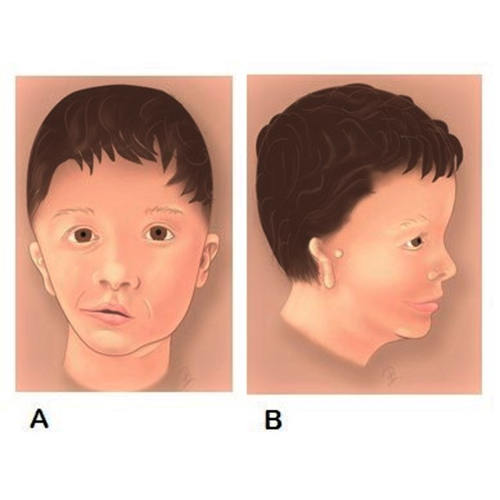
Hemifacial Microsomia (HFM) is a congenital condition where one side of the face is underdeveloped, usually affecting the ear, jaw, cheekbone, and sometimes the eye. It is the second most common facial birth defect after cleft lip and palate.
This condition can range from mild facial asymmetry to severe deformities that affect speech, hearing, chewing, and breathing. Surgical treatment is often needed to restore facial balance and function as the child grows.
What We Do
Our craniofacial surgery team provides personalized, staged surgical planning based on the age, severity, and growth pattern of the child. We focus on jaw reconstruction, ear reconstruction, and soft tissue correction to achieve a more balanced appearance and improved function.
Commonly Affected Areas
Lower jaw (mandible) – underdeveloped or missing bone
External ear – small, misshaped, or absent
Facial nerve – may cause weakness in facial movement
Cheek and soft tissues – flat or sunken appearance
Eye and mouth position – occasionally involved
Treatment Options
Distraction Osteogenesis – Gradual lengthening of the underdeveloped jaw
Rib Graft Mandibular Reconstruction – Using rib bone to reconstruct the jaw
Ear Reconstruction – Performed in stages (using cartilage or synthetic implants)
Orthodontics & Braces – For dental alignment and bite correction
Fat Grafting or Soft Tissue Augmentation – To restore facial contour
Speech, Hearing & Breathing Support – Through coordinated care
Benefits of Surgery
Restores facial symmetry
Improves jaw function, chewing, and bite
Enhances hearing and breathing in some cases
Boosts self-esteem and social comfort
Supports proper speech and language development
When is Surgery Performed?
Initial evaluation can begin in infancy
Major reconstructive surgeries typically start around age 5–8
Treatment may continue through adolescence as the child grows
Multidisciplinary care is essential for best outcomes
Recovery & Long-Term Care
Since HFM affects growth, children may need multiple surgeries over time. We offer continuous monitoring, growth assessments, and collaboration with ENT, orthodontics, audiology, and psychology teams for complete support.