Home / Hypertelorism
Drop Your Number here
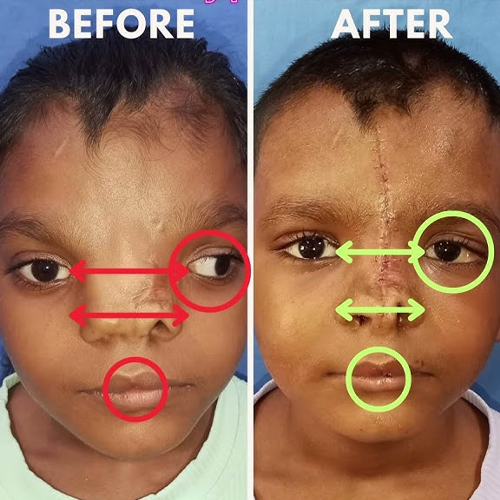
Hypertelorism is a craniofacial condition where there is an abnormally increased distance between the eyes. It may be present at birth (congenital) and often occurs as part of a syndrome or skull development disorder. While primarily cosmetic in nature, it can also affect vision, nasal structure, and self-confidence.
Surgical correction of hypertelorism helps restore facial symmetry, improves eye positioning, and supports psychosocial development, especially in children.
What We Do
Our craniofacial surgery team performs orbital box osteotomy or facial bipartition surgery, depending on the severity and associated conditions. These procedures involve carefully repositioning the eye sockets (orbits) by cutting and realigning facial bones using precision surgical techniques.
Who Needs This Surgery?
Children diagnosed with true orbital hypertelorism
Patients with craniofacial syndromes such as Crouzon, Apert, or frontonasal dysplasia
Individuals with nasal deformities and wide-set eyes
Those who experience social discomfort or facial asymmetry
Types of Surgical Techniques
Orbital Box Osteotomy – Moving both orbits inward and stabilizing with plates
Facial Bipartition – Used when midface and dental alignment correction is also needed
Forehead Remodeling – In some cases for improved forehead and orbital contour
Combined Nasal & Orbital Surgery – To achieve overall facial harmony
Benefits of Surgery
Brings eyes to a more natural position
Improves facial symmetry and balance
Enhances self-image and social interaction
Can improve vision-related issues in certain cases
Long-term, life-enhancing cosmetic and psychological results
Ideal Age for Surgery
Typically between 5 to 8 years of age, when facial growth allows safe correction
May vary based on associated syndromes or functional concerns
Risks and Recovery
Temporary swelling and bruising around the eyes
Risk of infection, bleeding, or relapse (rare with expert care)
Need for postoperative observation and sometimes further cosmetic refinement
Hospital stay of 5–7 days, followed by rest and gradual return to normal activity
Post-Surgical Care
Patients will be closely monitored with follow-up visits, imaging, and, if needed, psychological counseling or speech therapy support to ensure a holistic recovery.